
Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>



































> Insights > Differentiating Cytokine Detection Strategies in CAR-T vs. CAR-NK Therapies Cellular immunotherapies, including CAR-T and CAR-NK therapies, leverage engineered immune cells to combat cancer. While both modalities share similarities, their distinct biological mechanisms necessitate tailored approaches to cytokine and biomarker detection. CAR-T therapies heavily rely on IFN-γ as a central biomarker, whereas CAR-NK therapies require additional focus on Granzyme B, a key mediator of NK cell cytotoxicity. This article delineates the divergent detection strategies for CAR-T and CAR-NK therapies across drug development, Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC), and clinical trials.
CAR-T Therapies: IFN-γ as the Hallmark of T Cell Activation
• Functional Validation: IFN-γ is a primary indicator of CAR-T cell activation and cytotoxic potential. In vitro co-culture assays with tumor cells correlate IFN-γ secretion (measured via ELISA or flow cytometry) with target-specific killing, guiding CAR design optimizations (e.g., co-stimulatory domain selection).
• Safety Profiling: Elevated IFN-γ levels predict risks of cytokine release syndrome (CRS), prompting strategies like suicide gene switches (e.g., iCasp9) or dose titration.
CAR-NK Therapies: Dual Focus on IFN-γ and Granzyme B
• Functional Validation: NK cells exert cytotoxicity primarily through Granzyme B and perforin release. Unlike CAR-T cells, CAR-NK efficacy requires simultaneous detection of Granzyme B (direct apoptosis inducer) and IFN-γ (immune activation marker). For example, Granzyme B ELISA or intracellular staining post-target stimulation validates NK cell killing capacity.
• Safety Optimization: While CAR-NK therapies pose lower CRS risks than CAR-T, excessive Granzyme B may drive off-target tissue damage. Functional assays using primary hepatocytes or endothelial cells help assess cytotoxicity risks.
CAR-T Release Testing: IFN-γ-Driven Potency
• Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs): IFN-γ secretion is a mandatory potency marker. Batch consistency relies on stable IFN-γ levels, reflecting robust transduction and culture conditions. FDA/EMA guidelines mandate validated IFN-γ assays for potency.
• Stability Monitoring: IFN-γ retention during cryopreservation and thawing is critical for shelf-life determination.
CAR-NK Release Testing: Granzyme B as a Non-Negotiable CQA
• CQAs: CAR-NK potency requires dual verification of Granzyme B (cytotoxicity) and IFN-γ (activation). For "off-the-shelf" NK products, rapid Granzyme B quantification ensures readiness for clinical use.
• Process Sensitivity: NK cells are highly sensitive to freeze-thaw cycles. Granzyme B activity post-thawing is a key release criterion, ensuring functional resilience.
CAR-T: IFN-γ Dynamics Guide Clinical Management
• Efficacy: Early post-infusion IFN-γ surges correlate with durable responses in B-cell malignancies. Persistent low IFN-γ may signal poor CAR-T expansion or resistance.
• Toxicity: IFN-γ, alongside IL-6, drives CRS grading. Real-time monitoring informs interventions.
CAR-NK: Granzyme B as a Unique Efficacy/Toxicity Nexus
• Efficacy: High baseline Granzyme B levels in infused CAR-NK products associate with prolonged antitumor activity (e.g., in multiple myeloma). Post-treatment Granzyme B elevation in serum may indicate target engagement.
• Toxicity: Unlike CRS-driven IFN-γ, elevated Granzyme B may signal organ-specific toxicity (e.g., hepatotoxicity). Trials must establish safety thresholds via longitudinal monitoring.
The dichotomy between CAR-T and CAR-NK therapies extends to biomarker detection: while IFN-γ remains central to both, CAR-NK’s reliance on Granzyme B underscores its distinct biology and clinical profile. By tailoring detection strategies to these differences, developers can optimize product quality, mitigate risks, and accelerate the translation of both CAR-T and CAR-NK therapies into safer, more effective treatments. As the field advances, integrating novel technologies and biomarker insights will be pivotal in unlocking the full potential of cellular immunotherapy.
ACROBiosystems have launched ClinMax™ ready-to-use ELISA kits with rigorously quality control, ensuring the precision, stability, and consistency of the analysis results, to better meet your experimental needs.
ClinMax™ Human IFN-γ ELISA Kit, PRO (Cat. No. CEA-C006)
- Intra-Assay and Inter-Assay Precision: The CV of the measured quality control (QC) samples is all below 10%, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. (A) Intra-Assay Precision Data for CEA-C006; (B) Inter-Assay Precision Data for CEA-C006
- Sample Value: 208 healthy serum samples were evaluated for the concentrations of human IFN-γ in assay, as shown in Figure 2.
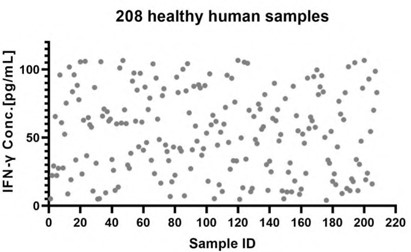
Figure 2. Quantification of IFN-γ in Human Serum via CEA-C006 ELISA Kit
ClinMax™ Human Granzyme B ELISA Kit (Cat. No. CEA-B033)
- Intra-Assay and Inter-Assay Precision: The CV of the measured quality control (QC) samples is all below 10%, as shown in Figure 3.
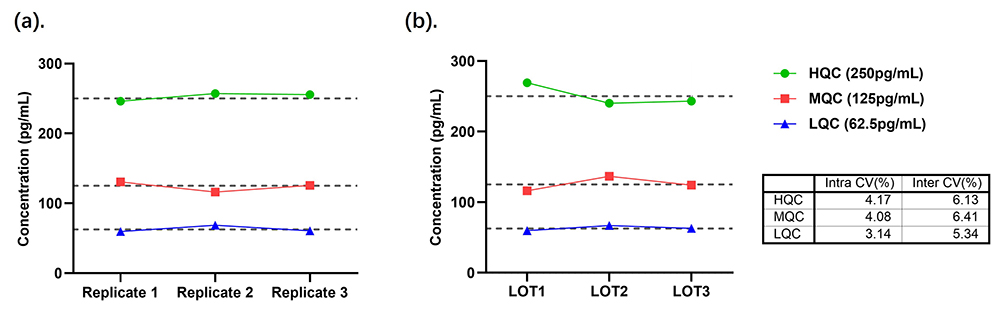
Figure 3. (A) Intra-Assay Precision Data for CEA-B033; (B) Inter-Assay Precision Data for CEA-B033
- Sample Value: Use PHA to stimulate PBMC cells for 1, 3, 5 days, then collect cell supernatant and detect GZMB concentration, the data was shown in Figure 4.
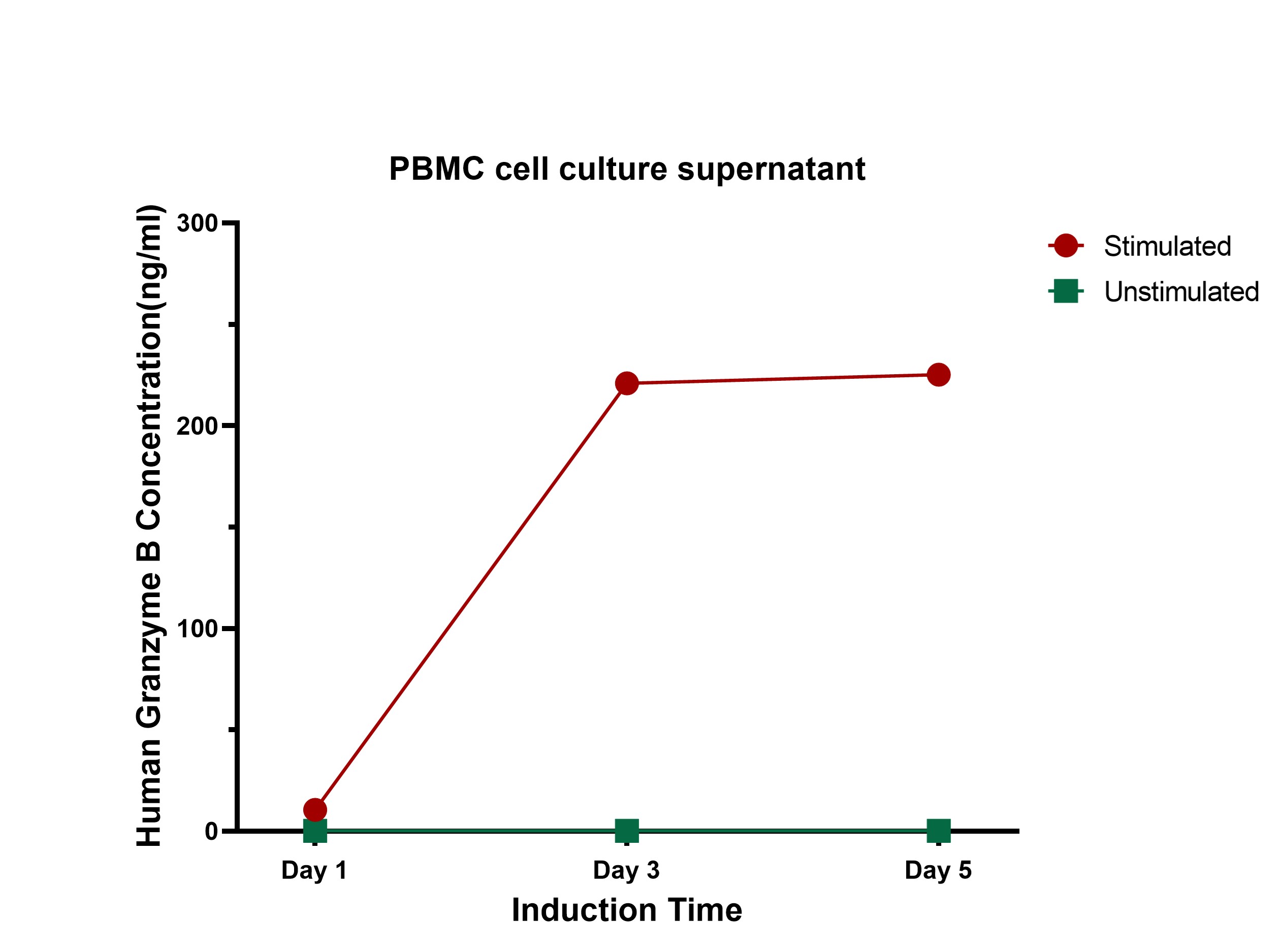
Figure 4. Quantification of GZMB in Cell Culture Supernatant via CEA-C033 ELISA Kit
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.







