
Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>



































> Insights > Evaluating Therapeutic Efficacy in Autoimmune Disease Biologic Development Biomarkers play a vital role in the development of biological drugs, offering insights into drug mechanisms of action (MOA), guiding clinical study design, and optimizing treatment strategies. Widely used across early discovery, preclinical, and clinical stages, biomarkers ensure precise dosing, efficacy evaluation, and accelerated drug development. This article introduces the mechanisms of action and biomarker research for biological drugs for autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune diseases are a key area of focus in biological drug research, owing to their well-characterized mechanisms and specific targets. Among the leading indications under development are rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, plaque psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), arthritis, and ulcerative colitis. These conditions collectively account for over 1,100 drug candidates currently in development pipelines.
The primary therapeutic targets in this field involve the TNF/IL-23/IL-17 axis, with critical biomarkers and cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-12/23p40, IL-23p19, IL-17A, IL-17F, and TL1A. Notable targeted drugs already on the market include Adalimumab, Ustekinumab, Secukinumab, Tildrakizumab, Guselkumab, and Risankizumab (Figure 1).
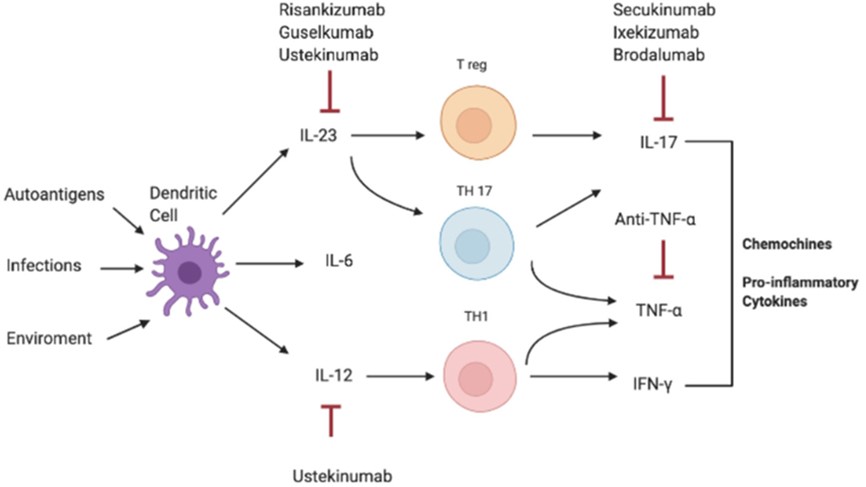
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of IL-17-correlated disease and different targets of therapy. (DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2021.637829)
Another key pathway is the type 2 inflammation response, mediated primarily by Th2 cells, type 2 innate lymphoid cells, and Th2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and IL-31. Relevant biomarkers include cytokines and targets like IL-4, IgE, IL-5, IL-13, IL-33, and TSLP (Figure 2). Currently marketed targeted drugs include Dupilumab, Lebrikizumab, and Mepolizumab.
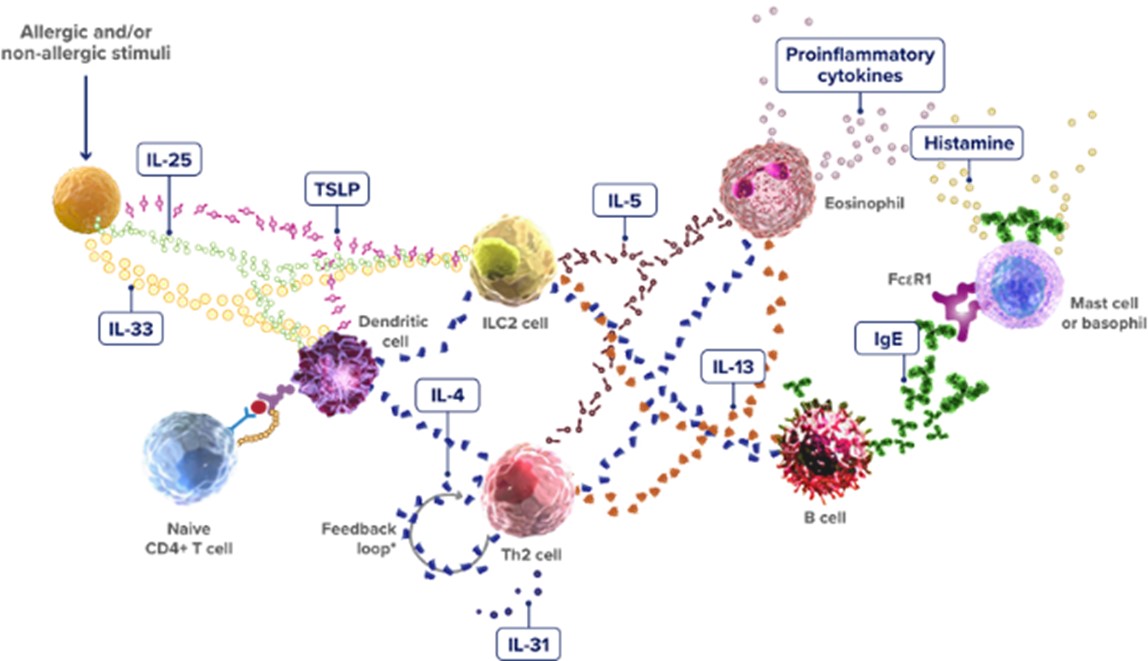
Figure 2 The Type 2 Inflammatory Pathway
(https://www.type2inflammation.com/resources/interactive-inflammation-pathway)
Cosentyx® (Secukinumab), an innovative biologic by Novartis, is a fully human IgG1/κ monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-17A (IL-17A). It is used to treat diseases such as plaque psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis.
Mechanism of Action
The IL-17 family comprises pro-inflammatory cytokines that mediate normal inflammatory and immune responses. IL-17 is primarily produced by T cells, particularly Th17 cells, but can also be triggered by mast cells and neutrophils. Among these, IL-17A is frequently upregulated in autoimmune diseases and is associated with chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disorders such as plaque psoriasis. IL-17A is more potent and has a higher affinity for IL-17 receptors than other family members like IL-17F. Secukinumab selectively binds to and inhibits IL-17A, blocking its interaction with IL-17 receptors and preventing the activation of related pro-inflammatory signaling pathways.
Biomarker Research in Clinical Trials
As detailed in the FDA’s Clinical Pharmacology and Biopharmaceutics Review, Secukinumab’s pharmacodynamics studies used biomarkers such as IL-17A, IL-17F, and human beta-defensin-2 (hBD-2) to assess drug efficacy by measuring their expression at the mRNA, protein, and tissue levels (Figure 3).
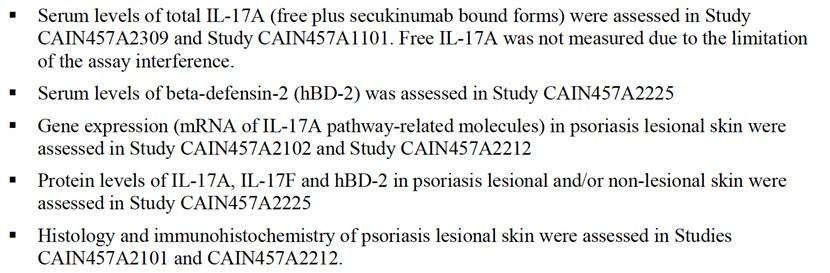
Figure 3 Summary of Clinical Pharmacodynamics
Dupixent® (Dupilumab) is a fully human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds to the IL-4 receptor, inhibiting its signaling pathway. As an IL-4 receptor α antagonist, Dupilumab blocks the signaling of pro-inflammatory cytokines implicated in allergic and atopic diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, asthma, and sinusitis with nasal polyps.
Mechanism of Action
In allergic and atopic conditions such as asthma, type 2 inflammation involves Th2 cell-mediated immune responses. Upregulation of the Th2/type 2 pathway is observed in various inflammatory diseases, with Th2 activation linked to the production of Th2-related cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13. IL-4 and IL-13 are pivotal in regulating type 2 inflammation, inducing conditions such as allergic rhinitis, asthma, and atopic dermatitis.
IL-4 has two receptor types: Type 1 receptor (IL-4Rα and γc chain) and Type 2 receptor (IL-4Rα and IL-13Rα1). IL-4Rα, a shared component of both receptor complexes, is broadly expressed in innate and adaptive immune cells, facilitating IL-4 and IL-13 signaling. Type 1 receptors are primarily expressed on lymphocytes and control Th2 cell differentiation, while Type 2 receptors are found on resident and myeloid cells. Dupilumab inhibits both IL-4 and IL-13 signaling by targeting IL-4Rα.
According to the FDA’s Clinical Pharmacology and Biopharmaceutics Review, Dupilumab’s pharmacodynamic evaluations included serum levels of IL-4 and IL-13 as standard PD markers. Additionally, exploratory evidence demonstrated reductions in serum concentrations of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17), total serum IgE, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) post-treatment (Figure 4).
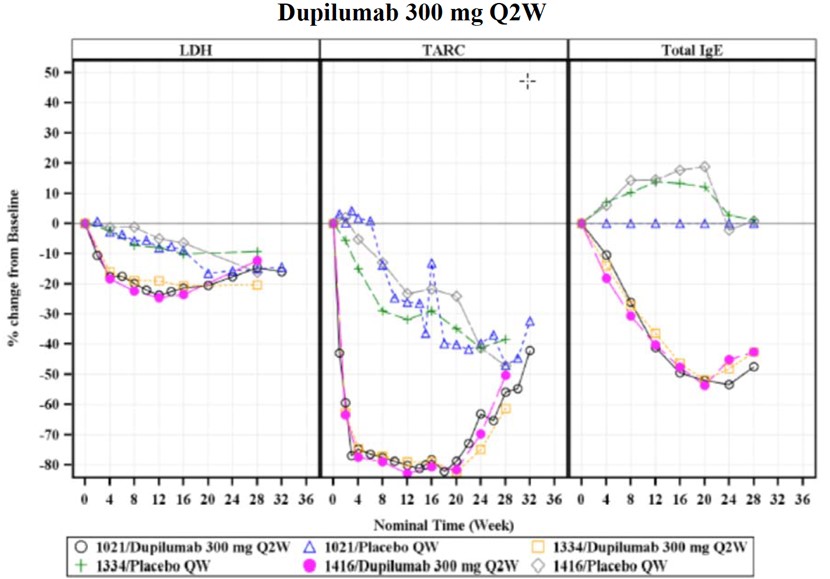
Figure 4 LDH, TARC/CCL17 and IgE changes (in percentage) from baseline under 300 mg Dupilumab treatment once per week, 16 weeks duration.
For biologics targeting the TNF/IL-23/IL-17 axis, key biomarkers such as IL-17A and IL-17F are essential across early research, preclinical, and clinical trial stages. Similarly, TARC/CCL17 serves as a critical biomarker for biologics aimed at the type 2 inflammatory pathway. Additional important biomarkers include cytokines like IL-12/IL-23p40, IL-23, IL-4, and IL-13. To support the advancement of targeted drug development for autoimmune diseases, ACROBiosystems offers a variety of ELISA kits for quantifying biomarkers, cytokines, and other analytes. These kits are validated with real samples to ensure accuracy, specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility in analytical results.
ClinMax™ Human TARC/CCL17 ELISA Kit (Cat. No. CEA-C029)
• Intra-Assay and Inter-Assay Precision: The CV of the measured quality control (QC) samples is all below 10%, as shown in Figure 5.
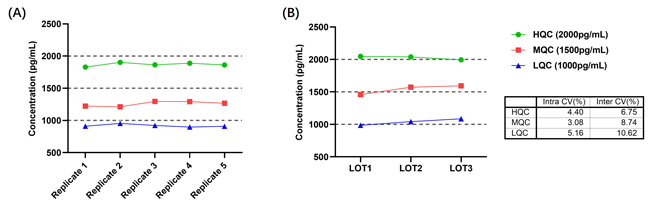
Figure 5. (A) Intra-Assay Precision Data for CEA-C029; (B) Inter-Assay Precision Data for CEA-C029
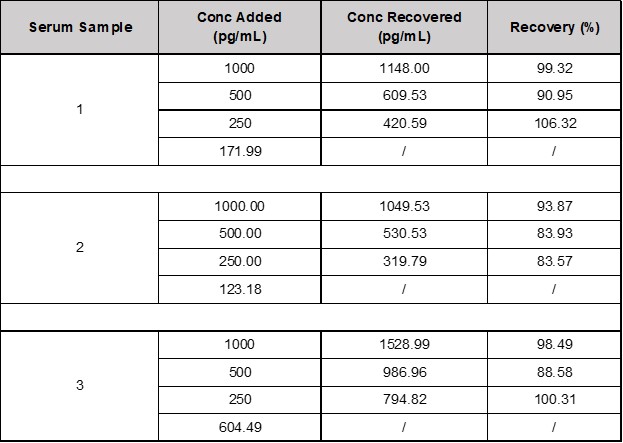
• Recovery: TARC/CCL17 was spiked into 3 human serum samples and then analyzed. The average recovery of TARC/CCL17 for serum samples is % (see Table 1).
Table 1. Recovery of TARC/CCL17 in Spiked Samples
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.







